Linux Ubuntu - korzystanie z pomocy
man
Nazwa pochodzi od ang. Manual – instrukcja obsługi. Służy do wyświetlania stron pomocy.
man <polecenie>
Przykładowo:
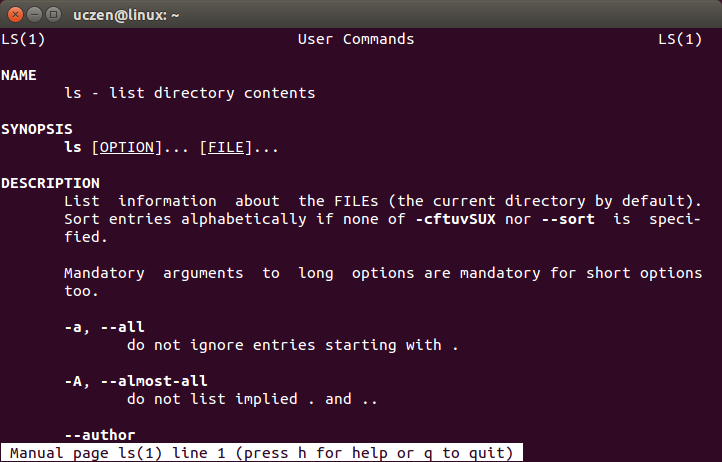
man ls
Aby wyjść z manuala należy nacisnąć q
Czasami nazwa nie jest jednoznaczna. Np. passwd oznacza polecenie do zmiany hasła, nazwę pliku oraz słuzy do obliczania haszy.
uczen@localhost:~$ man -f passwd passwd (5) - the password file passwd (1) - change user password passwd (1ssl) - compute password hashes uczen@localhost:~$ whatis passwd passwd (5) - the password file passwd (1) - change user password passwd (1ssl) - compute password hashes
Do sprawdzenia nazw służą polecenia man -f lub whatis
Po wpisanie man passwd standardowo załaduje się sekcja 1, czyli passwd (1). Jeśli chcemy np. poczytać sekcję 5, czyli na temat pliku z hasłami musimy wpisać man 5 passwd
W ogromie poleceń możemy zapomniać nazwę której szukamy. Tutaj z pomocą przychodzi man -k słowo_kluczowe
Przykładowo man -k permission zwróci nam polecenia związane z uprawnieniami.
uczen@localhost:~$ man -k permission access (2) - check real user's permissions for a file chmod (2) - change permissions of a file eaccess (3) - check effective user's permissions for a file euidaccess (3) - check effective user's permissions for a file faccessat (2) - check user's permissions of a file relative to a direc... faked (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... faked-sysv (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... faked-tcp (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... fchmod (2) - change permissions of a file fchmodat (2) - change permissions of a file relative to a directory f... ioperm (2) - set port input/output permissions
Zamiennie można użyć apropos permission
uczen@localhost:~$ apropos permission access (2) - check real user's permissions for a file chmod (2) - change permissions of a file eaccess (3) - check effective user's permissions for a file euidaccess (3) - check effective user's permissions for a file faccessat (2) - check user's permissions of a file relative to a direc... faked (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... faked-sysv (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... faked-tcp (1) - daemon that remembers fake ownership/permissions of fi... fchmod (2) - change permissions of a file fchmodat (2) - change permissions of a file relative to a directory f... ioperm (2) - set port input/output permissions
info
Wyświetla informacje o dokumentacji
info <polecenie>
Przykładowo:
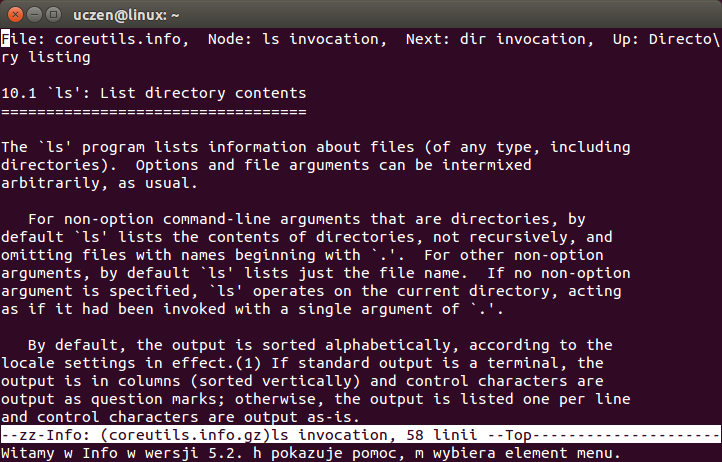
info ls
Użycie --help
polecenie --help
Przykładowo:
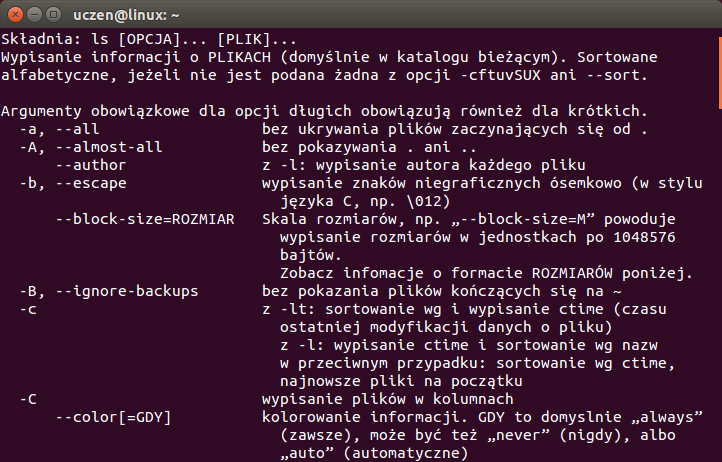
ls --help