Packet Tracer VLAN: Różnice pomiędzy wersjami
| (Nie pokazano 14 wersji utworzonych przez jednego użytkownika) | |||
| Linia 62: | Linia 62: | ||
Jak widać wszystkie porty należą do vlanu 1, czyli wszystkie podpięte hosty powinny się komunikować (oczywiście, jeśli zostały nadane adresy IP). | Jak widać wszystkie porty należą do vlanu 1, czyli wszystkie podpięte hosty powinny się komunikować (oczywiście, jeśli zostały nadane adresy IP). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dodamy dwa vlany o numerach 2 i 3 oraz nadamy im nazwy VLAN2 i VLAN3. We wcześniejszym przykładzie vlan2 nazywa się VLAN1 a vlan3 VLAN2, przypominam, aby nie było pomyłki przy porównywaniu zrzutów. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch#configure terminal | ||
| + | Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. | ||
| + | Switch(config)#vlan 2 | ||
| + | Switch(config-vlan)#name VLAN2 | ||
| + | Switch(config-vlan)#exit | ||
| + | Switch(config)#vlan 3 | ||
| + | Switch(config-vlan)#name VLAN3 | ||
| + | Switch(config)#exit | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Przypisujemy porty do vlanów. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch(config)#interface fastethernet0/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#exit | ||
| + | Switch(config)#int fa3/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#int eth4/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#exit | ||
| + | Switch(config)#int fa1/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#exit | ||
| + | Switch(config)#int fa2/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#exit | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
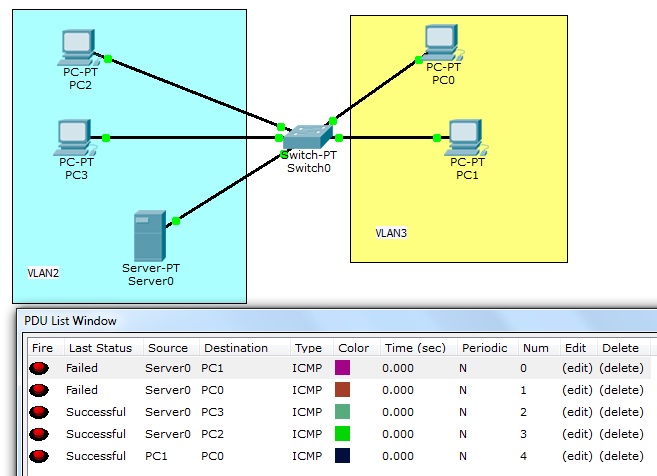
| + | Jak widać komunikują się tylko hosty w ramach swoich vlanów. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:vlan7.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Możemy ponowić polecenie <code>show vlan</code> lub <code>show vlan id NR</code> albo <code>show vlan brief</code>, aby sprawdzić czy pojawiły się utworzone przez nas sieci wirtualne. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch#show vlan brief | ||
| + | |||
| + | VLAN Name Status Ports | ||
| + | ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- | ||
| + | 1 default active Eth5/1 | ||
| + | 2 VLAN2 active Fa0/1, Fa3/1, Eth4/1 | ||
| + | 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 | ||
| + | 1002 fddi-default active | ||
| + | 1003 token-ring-default active | ||
| + | 1004 fddinet-default active | ||
| + | 1005 trnet-default active | ||
| + | Switch# | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Usuwanie interfejsów z sieci VLAN=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Usuniemy interfejs Fa0/1 z vlanu 2, czyli tym samym usuniemy z tej sieci vlan Server0. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch#conf t | ||
| + | Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. | ||
| + | Switch(config)#int fa0/1 | ||
| + | Switch(config-if)#no switchport access vlan 2 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sprawdzamy | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch#show vlan brief | ||
| + | |||
| + | VLAN Name Status Ports | ||
| + | ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- | ||
| + | 1 default active Fa0/1, Eth5/1 | ||
| + | 2 VLAN2 active Fa3/1, Eth4/1 | ||
| + | 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 | ||
| + | 1002 fddi-default active | ||
| + | 1003 token-ring-default active | ||
| + | 1004 fddinet-default active | ||
| + | 1005 trnet-default active | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Usuwanie sieci VLAN=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch(config)#no vlan 2 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sprawdzamy | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Switch#show vlan brief | ||
| + | |||
| + | VLAN Name Status Ports | ||
| + | ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- | ||
| + | 1 default active Fa0/1, Eth5/1 | ||
| + | 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 | ||
| + | 1002 fddi-default active | ||
| + | 1003 token-ring-default active | ||
| + | 1004 fddinet-default active | ||
| + | 1005 trnet-default active | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
[[Category:Cisco Packet Tracer]] | [[Category:Cisco Packet Tracer]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Sieci komputerowe]] | ||
Aktualna wersja na dzień 13:54, 17 mar 2014
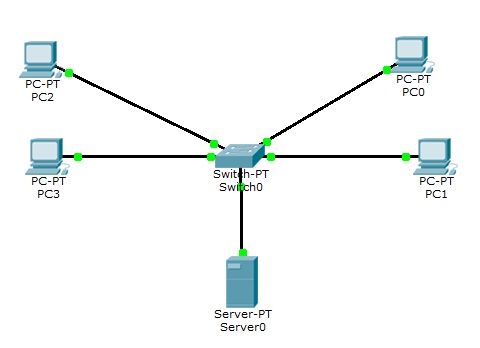
W programie Packet Tracer stworzymy lokalne sieci wirtualne czyli VLANy.
Mamy zwykłą sieć LAN. Komputery są odpowiednio skonfigurowane do pracy w sieci.
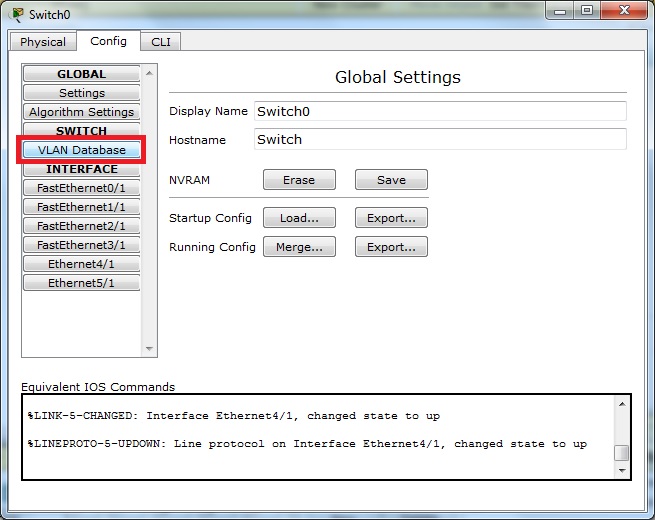
Konfigurowanie VLANów poprzez GUI Packet Tracer
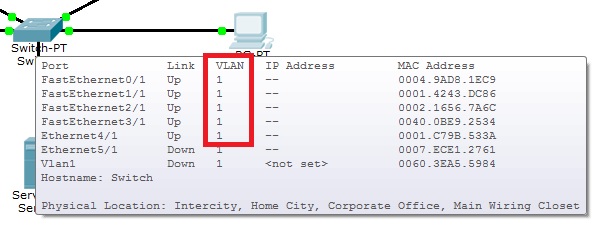
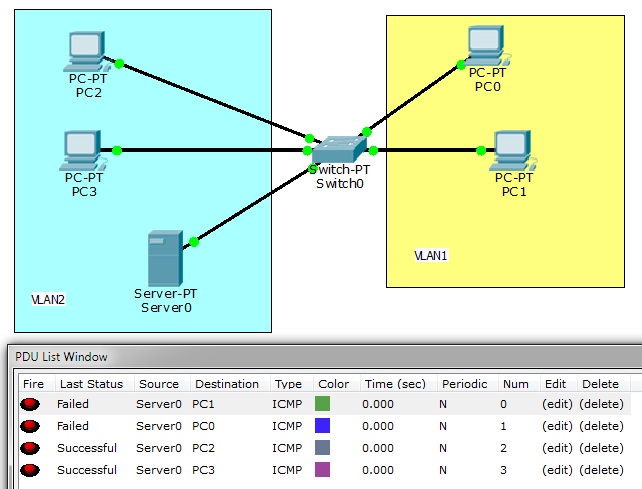
Jak widać na tablicy przełączania komputery się "widzą". Należą do jednego VLANu.
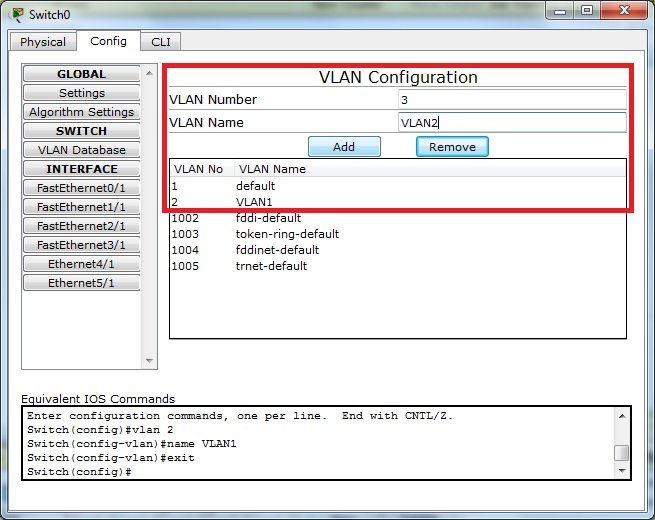
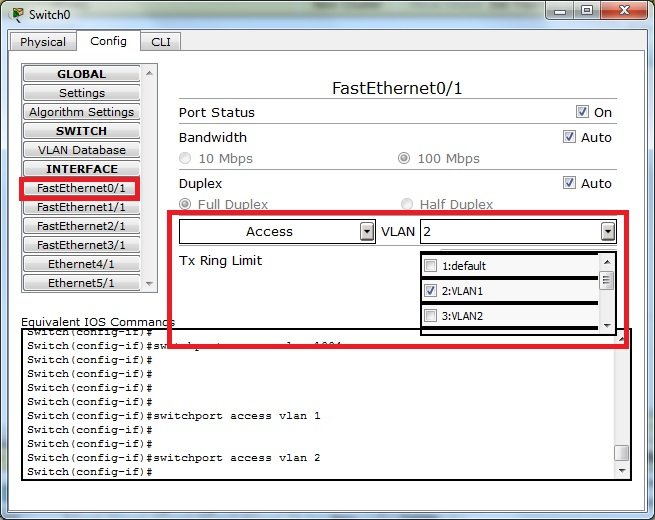
Na switchu dodajemy 2 sieci wirtualne, VLAN1 i VLAN2
Przypisujemy porty switcha do odpowiednich VLANów
Jak widać komputery z różnych sieci wirtualnych nie widzą się. Pingi nie przechodzą.
Konfigurowanie VLANów poprzez CLI
Sprawdzamy jakie posiadamy VLANy na przełączniku. Służy do tego polecenie show vlan
Switch>enable
Switch#show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa1/1, Fa2/1, Fa3/1
Eth4/1, Eth5/1
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
Remote SPAN VLANs
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
Switch#
Jak widać wszystkie porty należą do vlanu 1, czyli wszystkie podpięte hosty powinny się komunikować (oczywiście, jeśli zostały nadane adresy IP).
Dodamy dwa vlany o numerach 2 i 3 oraz nadamy im nazwy VLAN2 i VLAN3. We wcześniejszym przykładzie vlan2 nazywa się VLAN1 a vlan3 VLAN2, przypominam, aby nie było pomyłki przy porównywaniu zrzutów.
Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#vlan 2 Switch(config-vlan)#name VLAN2 Switch(config-vlan)#exit Switch(config)#vlan 3 Switch(config-vlan)#name VLAN3 Switch(config)#exit
Przypisujemy porty do vlanów.
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#int fa3/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#int eth4/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#int fa1/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3 Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#int fa2/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3 Switch(config-if)#exit
Jak widać komunikują się tylko hosty w ramach swoich vlanów.
Możemy ponowić polecenie show vlan lub show vlan id NR albo show vlan brief, aby sprawdzić czy pojawiły się utworzone przez nas sieci wirtualne.
Switch#show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Eth5/1 2 VLAN2 active Fa0/1, Fa3/1, Eth4/1 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 1002 fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active Switch#
Usuwanie interfejsów z sieci VLAN
Usuniemy interfejs Fa0/1 z vlanu 2, czyli tym samym usuniemy z tej sieci vlan Server0.
Switch#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#int fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#no switchport access vlan 2
Sprawdzamy
Switch#show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Eth5/1 2 VLAN2 active Fa3/1, Eth4/1 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 1002 fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active
Usuwanie sieci VLAN
Switch(config)#no vlan 2
Sprawdzamy
Switch#show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Eth5/1 3 VLAN3 active Fa1/1, Fa2/1 1002 fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active