Wstęp do IOS CISCO: Różnice pomiędzy wersjami
| Linia 117: | Linia 117: | ||
Jak widać znak '''?''' stawiamy po spacji. | Jak widać znak '''?''' stawiamy po spacji. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Przykładowa konfiguracja== | ||
[[Category:Cisco Packet Tracer]] | [[Category:Cisco Packet Tracer]] | ||
Wersja z 17:49, 10 gru 2013
IOS,czyli Internetwork Operating System został opracowany przez firmę Cisco. Służy do konfigurowania urządzeń sieciowych tej firmy, jak rutery czy przełączniki. Ten system operacyjny nie ma interfejsu graficznego, pracuje się w wierszu poleceń, czyli CLI.
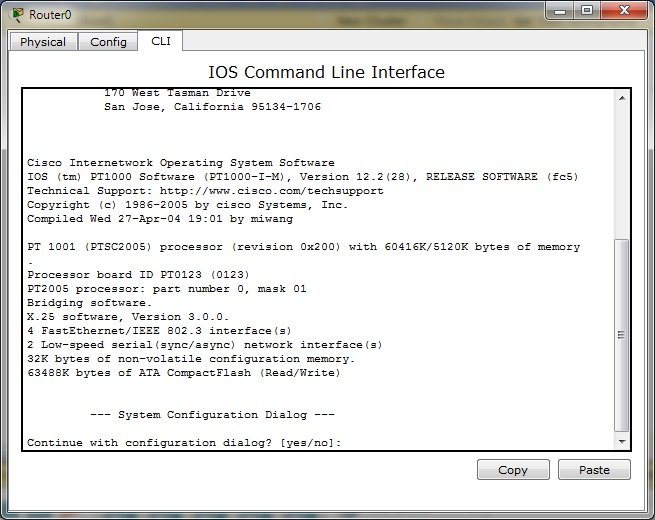
Poniżej obrazek przedstawiający dostęp do CLI IOS w programie Packet tracer
Pomijamy dialog konfiguracji systemu.
--- System Configuration Dialog --- Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no
Ruter zgłasza się w trybie użytkownika, świadczy o tym znak >
Router>
Aby wejść do trybu uprzywilejowanego piszemy enable. Aby z niego wyjść piszemy disable
Router>enable Router#disable Router>enable Router#
Symbolem trybu uprzywilejowanego jest #
Sprawdźmy do jakich poleceń mamy dostęp w trybie użytkownika. Służy do tego ?
Router>? Exec commands: <1-99> Session number to resume connect Open a terminal connection disable Turn off privileged commands disconnect Disconnect an existing network connection enable Turn on privileged commands exit Exit from the EXEC logout Exit from the EXEC ping Send echo messages resume Resume an active network connection show Show running system information ssh Open a secure shell client connection telnet Open a telnet connection terminal Set terminal line parameters traceroute Trace route to destination
Jak widać w tym trybie nie zmienimy konfiguracji rutera, możemy głównie wyświetlać informacje.
W trybie uprzywilejowanym mamy dostęp do pełni poleceń.
Router#? Exec commands: <1-99> Session number to resume auto Exec level Automation clear Reset functions clock Manage the system clock configure Enter configuration mode connect Open a terminal connection copy Copy from one file to another debug Debugging functions (see also 'undebug') delete Delete a file dir List files on a filesystem disable Turn off privileged commands disconnect Disconnect an existing network connection enable Turn on privileged commands erase Erase a filesystem exit Exit from the EXEC logout Exit from the EXEC mkdir Create new directory more Display the contents of a file no Disable debugging informations ping Send echo messages reload Halt and perform a cold restart resume Resume an active network connection rmdir Remove existing directory send Send a message to other tty lines setup Run the SETUP command facility show Show running system information ssh Open a secure shell client connection telnet Open a telnet connection terminal Set terminal line parameters traceroute Trace route to destination undebug Disable debugging functions (see also 'debug') write Write running configuration to memory, network, or terminal
Helpa, czyli ? możemy używać także przy wprowadzaniu poleceń. Uzyskamy podpowiedź.
Router#cl? clear clock Router#clock? clock Router#clock ? set Set the time and date Router#clock set ? hh:mm:ss Current Time Router#clock set 18:42:00 ? <1-31> Day of the month MONTH Month of the year Router#clock set 18:42:00 12 ? MONTH Month of the year Router#clock set 18:42:00 december ? <1-31> Day of the month Router#clock set 18:42:00 december 10 ? <1993-2035> Year Router#clock set 18:42:00 december 10 2013 Router#
Jak widać znak ? stawiamy po spacji.